About Activity
The Naval Industry, Shipbuilding and the related supply chain in Adriatic-Ionian region (EUSAIR) manufacturing industry, the Fourth Industrial Revolution and new digital age called Industry 4.0. The solution is to implement new technologies brought by the Industry 4.0 such as Cyber Security, Augmented Reality, Big Data and Analytics, Advanced Manufacturing, Additive Manufacturing, Cloud Computing.
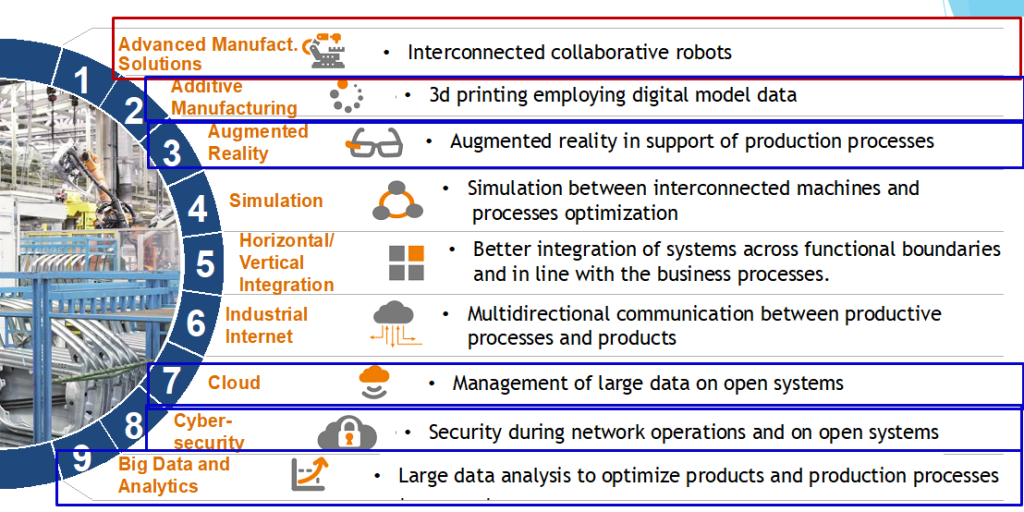
Future 4.0 project responded to the current challenges of the manufacturing industry of the shipyard and nautical logistic supply chain by developing a Smart Learning Model, as experimental methodology addressed to the companies operating in the Naval Industry, Shipbuilding and the related supply chain, with the aim to support their transition toward Industry 4.0 and break barriers to innovation.
The Smart Learning Model is based on the concept of “knowledge transfer for innovation” approach. The importance of the knowledge transfer for innovation was stressed for the first time at European level by the Green Paper on Innovation, published on 1995:
“….The road through which Europe can become a truly competitive economy is by improving its ability to produce knowledge through research, spreading it through education and continuous training and applying it through innovation”.
The starting point of the Knowledge Transfer approach there is the so-called “Knowledge triangle” that highlights the relationship of interaction between Education, Research and Innovation, considered the fundamental drivers for the development of a knowledge-based society.
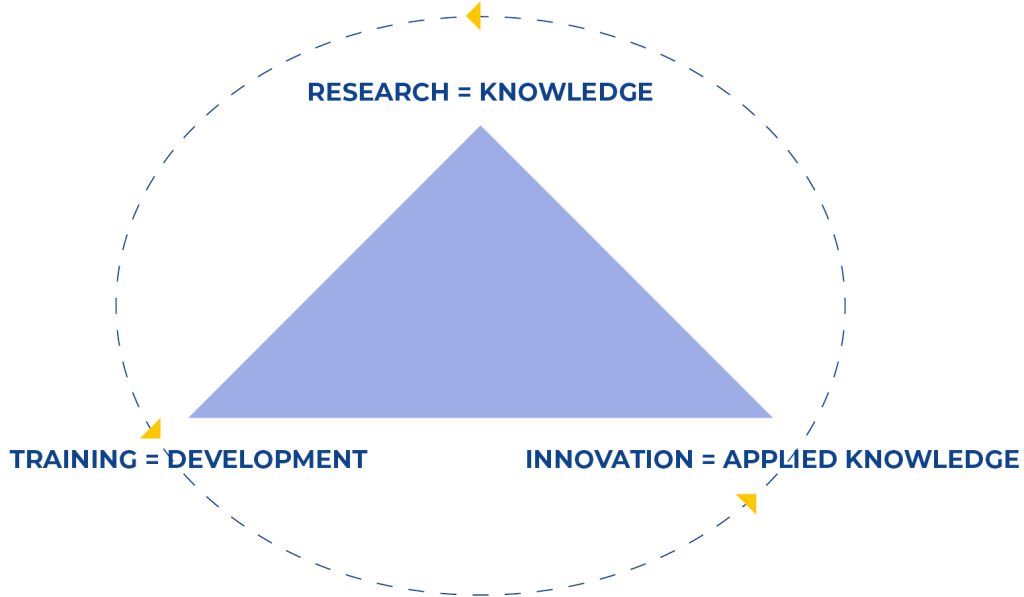
The knowledge triangle concept, which therefore refers to the needed integration of innovation, research (and technology) and (higher) education is at the base of all the EU innovation networks and clusters, as well as of the SIAV Factory of Knowledge and LMS approach. Champica Liyanage, some years later, took as point of reference the “knowledge triangle concept” to develop the so call Liyanage model, which clearly explicate the whole knowledge transfer process articulating it in 5 main phases.
The reference assumption of the Liyanage model is that “the acquired knowledge requires some sort of a conversion of knowledge in order to make it “useful” for innovation. Every knowledge transfer implies a TRANSFORMATION: a knowledge has value when it generates innovation and it is put into ACTION in a specific context. Transfer and adaptation become transformation as both technology and knowledge are transferred into new operational and managerial organizational contexts.
The FUTURE 4.0 project main aim has been to test and experiment the concept of “knowledge transfer for innovation” in over 100 companies active and operating in the Naval Industry, the Shipbuilding and the related supply chain, by the implementation of a piloting phase structured in 5 Local Pilot Actions, in Italy (Veneto and Apuilia region), Croatia, Albania and Greece.
Experimenting the knowledge transfer activities for the Validation of the FUTURE 4.0 Smart Learning Model, given the complexity of knowledge transfer processes from the industrial point of view, meant acting according to the learning model developed by Champica Liyanage and Bernardi, Garengo, Bettiol, focusing and foreseeing customized company and intercompany interventions on the 3 main phases of:
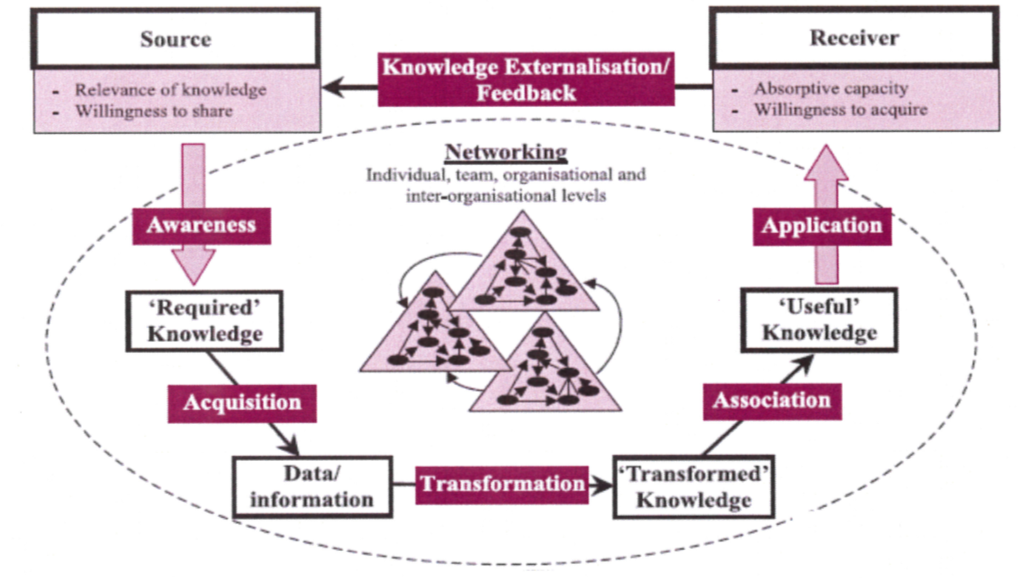
According to the Lyanage model it is the phase in which the company identifies the new knowledge deemed most appropriate to use and that responds adequately to its innovation needs. It is a critical phase since there are many options on the global market. In the FUTURE 4.0 experimental knowledge transfer activities it corresponded to the provision to target companies of basic knowledge and potential applications for advance manufacturing skills regarding KETs enabling technologies, selected in the previous Analysis project phase, through actions of awareness – mostly seminars and webinars – of main technological megatrends also related Green Manufacturing and Logistics. In this phase were involved not only the companies but also public institutions, research centres and universities and business organisation representatives, associations based on quadruple helix system approach.
In this phase the company identifies the “supplier” of knowledge deemed most credible and accessible. It refers to the company’s ability to identify and acquire the knowledge which is essential to be done. In the FUTURE 4.0 piloting phase, according to the Lyanage model, it has been translated in personalized in-company interventions (16 hours each), held mainly in blended learning methodology, in order to provide a deeper knowledge on one or more selected KETs technologies for company’s product and process innovation. In detail theoretical and intermediate knowledge was provided for its application into company real context and reality, by experts studying the specific situation of the company in advance and developing a strategy for its implementation.
As pointed out by Champica Liyanage the acquired knowledge requires it to be processed, “worked out” so that it can become usable by the company. Following the Lyanage reference model, the main purpose of the implemented FUTURE 4.0 transformation in-company personalized interventions (32 hours each), foreseen in each Local Pilot Action, was to support the applied knowledge into companies of innovation of products, processes and logistics in terms of Industry 4.0 and digitalisation. Advance knowledge transfer on selected KETs was therefore provided for their concrete applications on specific process and product as well as a personalized ad hoc plan by experts to better direct each company to the I4.0 world and to facilitate the integration of one or more technologies into the heritage of already existing business model. The development of Smart Learning Model and the implementation of the 5 Local Pilot Actions has been led and coordinated by Confindustria Veneto SIAV, as FUTURE 4.0 as partner in charge of the piloting phase and related methodological phase.
